Your cart is currently empty!
Category: Crypto
“Discover the latest trends and insights in cryptocurrency. Stay updated with news on Bitcoin, blockchain technology, crypto trading tips, and market analysis to make informed investment decisions.”

US Dollar: Trade Tensions, Fed Uncertainty Could Push Greenback Toward New Lows
- US Dollar faces heightened risks politically and economically; investors flock to safe-haven assets.
- Trump’s economic policies and Fed tensions contribute to dollar’s market volatility and depreciation.
- Persisting trade tensions and unpredictable policies accelerate shifts from dollar to other currencies.
- Looking for actionable trade ideas to navigate the current market volatility? Subscribe here to unlock access to InvestingPro’s AI-selected stock winners.
Recently, the has been encountering rising risks both politically and economically. The US Dollar Index reached its lowest point in three years, dropping below 98 on the week’s first trading day. This trend indicates that investors are shifting away from the dollar in favor of safe-haven assets.
Tensions Between Trump and Powell Disrupt the US Dollar
President Donald Trump’s threat of impeachment against Fed Chairman Jerome Powell played a major role in the dollar’s depreciation. Trump’s emphasis that Powell’s removal “can’t happen fast enough” is seen as not only a political message but also a challenge to the Fed’s independence. This is priced as a systemic risk by the markets.
The Fed’s decision to keep unchanged shows that it prioritizes the fight against inflation, while Trump wants a looser monetary policy to support growth. The conflict between these two different approaches increases uncertainties regarding monetary policy.
Political pressure on the Fed is having a profound impact not only on bond markets but also on FX markets. Trump’s aggressive rhetoric is undermining the dollar’s status as a “safe haven”. Investors reduced their holdings of US assets in their portfolios and accelerated their shift towards alternative currencies such as , and .
The fell from a peak of 110 after Trump’s election victory to 98 today. This decline can also be seen as evidence that Trump is moving away from the precious dollar policy. The “strong dollar” rhetoric advocated by the White House in the past has been replaced by a competitive devaluation strategy. As a result, the Trump administration has begun to move from the precious dollar to the worthless dollar phase in trade wars.
Global Trade Tensions and Volatility
Chicago Fed President Austan warned over the weekend that tariffs could have a negative impact on economic activity until the summer months, a statement that also confirmed concerns about growth.
Trump’s global trade policies also continue to put pressure on the dollar. In particular, the lack of a concrete negotiation step with China and the inconclusive negotiations with countries such as Japan increase global uncertainty.
In this environment, US multinationals have started to extend the maturities of their foreign exchange hedges. This shows that they are defending against not only short-term but also medium and long-term dollar fluctuations. While some companies have extended their hedge maturities to 2-5 years, this strengthens the comments that the perception of weakness on the dollar is not temporary and is becoming structural.
US Dollar’s Technical Outlook
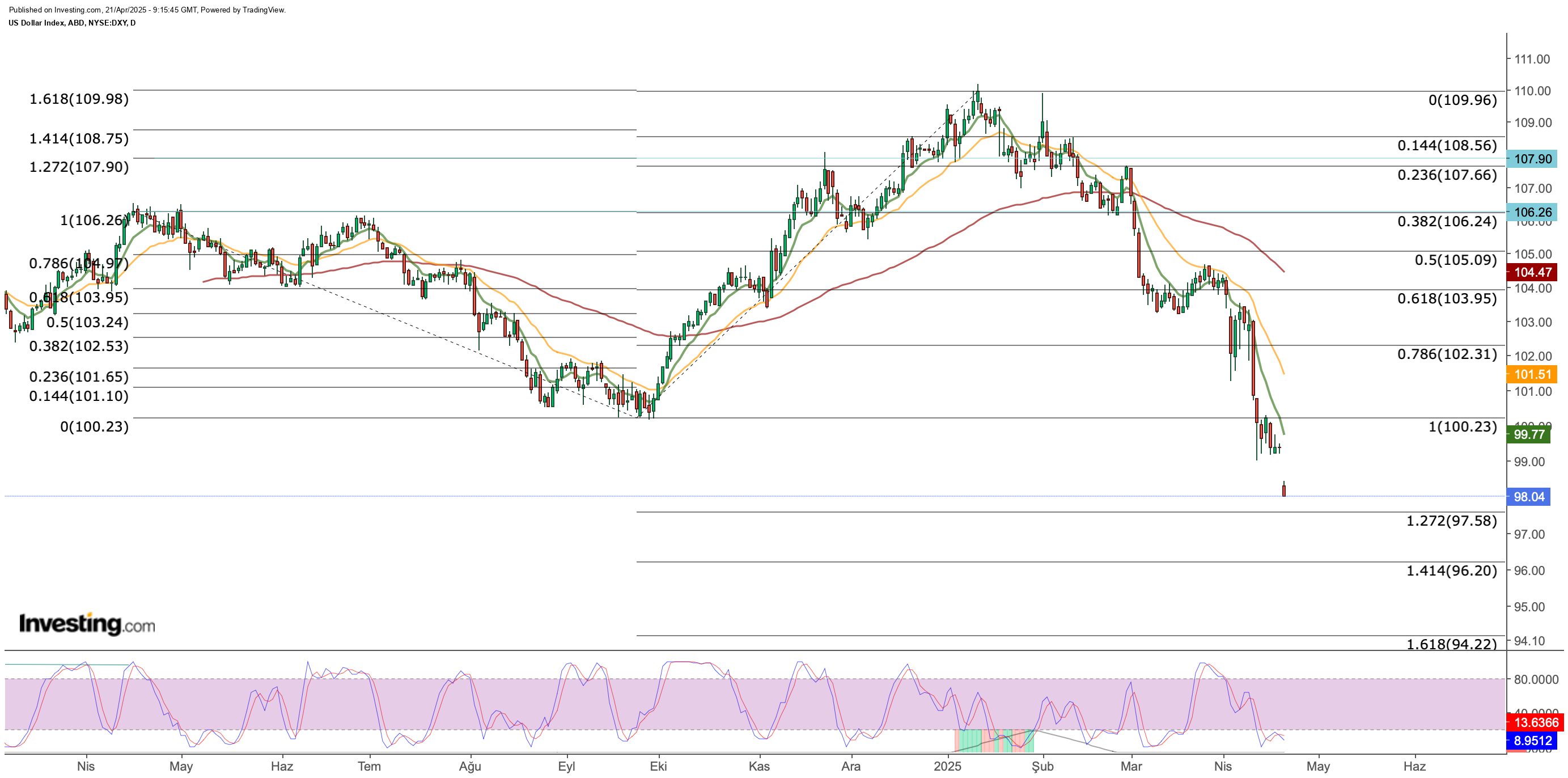
The dollar started the week at 98.30, down more than 1% due to Trump’s harsh rhetoric against Fed Chairman Powell, and maintained its bearish outlook in the first hours.
The last downtrend in the dollar found support at the 100 level in the last quarter of 2024. In the ongoing process, Trump’s election as US President and the strong dollar perception helped the dollar to rise rapidly against six major currencies. However, Trump’s aggressive growth policy and global tariff plans created serious uncertainty in the short term.
Since the start of the year, the DXY has been declining steadily, recently breaking the psychological support level at 100 and continuing its sharp fall. From a technical perspective, the last upward trend concluded in the Fibonacci expansion area (between Fib 1.272 and Fib 1.618). The downward trend, which began from the 110 peak in January, is now moving towards the Fibonacci expansion area once more, reflecting the most recent rise.
In this scenario, the level of 97.5 (Fib 1.272) will be an important support to watch. If this support level is broken, the downward movement might continue and find a possible endpoint in the 94-97 range. However, if the DXY holds steady around the 97 level, there could be an increase in buying interest, potentially driving it back up toward the 100 level. Despite this possibility, the current technical indicators suggest that the bearish trend is stronger at the moment.
Trump’s Influence on Dollar’s Direction Persists
President Trump remains a key factor influencing the dollar’s direction. As the election period begins, markets are actively factoring in Trump’s economic policies and his attempts to influence the Fed. Despite this, the Fed remains committed to prioritizing price stability and combating inflation over promoting growth.
In this contentious environment, investors are distancing themselves from the dollar, focusing more on the uncertainties within the US economy, even though the Fed is inclined to maintain high interest rates. If this trend persists, the dollar may continue to weaken.
****
Be sure to check out InvestingPro to stay in sync with the market trend and what it means for your trading. Whether you’re a novice investor or a seasoned trader, leveraging InvestingPro can unlock a world of investment opportunities while minimizing risks amid the challenging market backdrop.
Subscribe now and instantly unlock access to several market-beating features, including:
- ProPicks AI: AI-selected stock winners with proven track record.
- InvestingPro Fair Value: Instantly find out if a stock is underpriced or overvalued.
- Advanced Stock Screener: Search for the best stocks based on hundreds of selected filters, and criteria.
- Top Ideas: See what stocks billionaire investors such as Warren Buffett, Michael Burry, and George Soros are buying.

Disclaimer: This article is written for informational purposes only. It is not intended to encourage the purchase of assets in any way, nor does it constitute a solicitation, offer, recommendation or suggestion to invest. I would like to remind you that all assets are evaluated from multiple perspectives and are highly risky, so any investment decision and the associated risk rests with the investor. We also do not provide any investment advisory services.

Now is not the time for a restaking revival

Opinion by: Alon Muroch, founder of SSV Labs
Even though Ethereum remains a leader in terms of total value locked (TVL), things aren’t looking great. Network activity is hemorrhaging, and momentum is slipping. Ethereum has become locked in a fight for its future. Without meaningful change, Ethereum risks becoming inaccessible to the builders and users it needs to thrive. Ethereum needs fresh ideas to bolster the ecosystem out of its slump, unify it, and genuinely support innovation.
Enter based applications (bApps), which are any application or service that uses the Ethereum validator set for security. Inspired by the based movement, bApps enable any project to bootstrap directly from the Ethereum layer 1 (L1), enabling interoperable, scalable and cost-effective development.
High stakes and high costs
The recent decline in network activity highlights a deep issue across Ethereum, and it boils down to UX. The race to scale a blockchain isn’t just about TVL and transactions per second (TPS). It’s about the experience of users and developers who co-create the ecosystem. Ease of development and interoperable developer ecosystems and applications are paramount. Improving the developer experience is crucial for improving user experience, which drives adoption.
Today, builders are presented with two options. The first and more popular one is restaking, which has become the default mechanism for bootstrapping new services by locking up validators’ withdrawal keys or large amounts of capital for security. That leaves teams with only one other inconvenient alternative: self-bootstrapping. Building a validator set from scratch is resource-heavy, technically complex and often starts off centralized. Both choices are limiting for builders and don’t solve the fragmentation problems we see today in Ethereum.
It is not just builders but validators that are affected by this system. In the current restaking setup, validators who want to earn more yield by supporting new services must restake, lock up their withdrawal keys, and take on additional risk. By locking up withdrawal keys to secure applications with slashable capital, validators are exposed to cascading risks, which, at scale, could affect Ethereum itself — a core departure from Ethereum’s founding vision.
bApps are more secure
bApps provide a third, more accessible option for self-bootstrapping and restaking. Using based security infrastructure drastically lowers entry barriers for any size protocol to build securely and sustainably, all while preserving the traditional network effects of Ethereum. Validators are incentivized to join through risk-free yield opportunities; developers can affordably access security to build; and users benefit from a unified and interoperable ecosystem.
Recent: SSV Network to create ‘based’ apps infrastructure for Ethereum
Mission-critical services like rollups, bridges and oracles don’t need to reinvent the wheel. They simply plug into an existing, trusted security model. Using Ethereum validators as a primary security base, any out-of-protocol service can inherit the Ethereum L1’s decentralization and Sybil resistance. It’s also possible to extend this paradigm beyond Ethereum, enabling other L1 validators to secure bApps. This potentially turns bApps into a marketplace for multichain security, dramatically reducing the complexity (and cost) for developers and raising the bar for the entire ecosystem, offering a “based” path forward.
bApps empower validators to earn more with their existing stake. By primarily using the validator principle as non-slashable security, validators can opt into many services through their existing Ethereum validator role without needing to restake or supply extra stakes. This would encourage broader validator participation, especially from smaller or more risk-averse operators, which is excellent considering solo stakers are an important ecosystem pillar.
bApps unlock scalability
bApps also revolutionize Ethereum’s current bootstrapping ecosystem, which relies heavily on slashable capital. In restaking, one participant’s gain may directly correspond to another’s loss, creating a zero-sum model. Building a competitive dynamic where participants must add or reallocate resources instead of sharing them, consequently working against new entrants by creating competition for limited attention and resources.
The based economy, conversely, promotes an infinite-sum game, transforming competition for resources into a synergistic environment where new applications, services and participants increase the overall value of the platform. Each new validator increases security for bApps, and each new bApp provides new opportunities for validators. This infinitely scalable model breaks free from the limitations of a zero-sum model, enabling seamless bootstrapping, rewarding innovation and building more secure, inclusive and resilient ecosystems.
Unifying Ethereum’s fractured ecosystem
For Ethereum to grow, fragmentation has to be addressed. Builders need building blocks, which need to be secure, low-cost, interoperable and scalable. Think about what cloud computing did for Web2. BApps offer just that — by introducing an infinite-sum game, they unlock scalability and provide a safe and affordable way to bootstrap with Ethereum’s proof-of-stake network.
If Ethereum is to be the foundation of tomorrow’s decentralized world, it must empower the builders of today. The way forward is to solve Ethereum’s user and developer experience problem with a based infrastructure. Going based is the clear solution.
Opinion by: Alon Muroch, founder of SSV Labs.
This article is for general information purposes and is not intended to be and should not be taken as legal or investment advice. The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed here are the author’s alone and do not necessarily reflect or represent the views and opinions of Cointelegraph.

South Korean crypto emerges from failed coup into crackdown season
South Korea kicked off 2025 with political chaos, regulatory heat and a crypto market finally brought to heel — or at least forced to grow up.
The nation closed 2024 in disarray following then-President Yoon Suk Yeol’s botched martial law stunt in December.
In the aftermath, authorities spent the first quarter drawing lines in the sand as financial watchdogs slapped cryptocurrency exchanges with probes and lifted the ban on corporate trading accounts. Meanwhile, crypto adoption hit record highs as trading volume cooled.
Here’s a breakdown of the key developments that shaped South Korea’s crypto sector in Q1 of 2025.
South Korea’s economy limped into 2025 as local currency tanked. Source: Ki Young Ju South Korean crypto traders given yet another two-year tax exemption
Jan. 1 — Crypto tax postponed
A planned 20% capital gains tax on crypto did not take effect on Jan. 1 after lawmakers agreed to delay it until 2027. This was the third postponement: first from 2022 to 2023, then again to 2025.
Related: Crypto’s debanking problem persists despite new regulations
The latest delay, reached through bipartisan consensus in late 2024, came amid mounting economic uncertainty and political turmoil. Lawmakers cited fears of investor flight to offshore exchanges, challenges in tracking wallet-based profits, and shifting national priorities in the wake of Yoon’s failed martial law stunt and subsequent impeachment.
Jan. 14 — Warning against North Korean crypto hackers
The US, Japan and South Korea published a joint statement on North Korean crypto hacks. Crypto firms were warned to guard against malware and fake IT freelancers. Lazarus Group, the state-sponsored cyber threat group, was named as a prime suspect in some of the top hacks in 2024, such as the $230-million hack on India’s WazirX and the $50-million hack against Upbit, South Korea’s largest crypto exchange.
At least $1.34 billion of crypto stolen in 2024 has been attributed to North Korea. Source: Chainalysis Jan. 15 — Companies wait on the sidelines for crypto greenlight
South Korea’s Virtual Asset Committee, a crypto policy coordination body under the Financial Services Commission (FSC), held its second meeting. The FSC was widely expected to approve corporate access to trading accounts on local exchanges. Despite popular demand, the FSC held off on making an official decision, citing the need for further review.
Instead, the FSC announced investor protections against price manipulation and stricter stablecoin oversight.
Jan. 16 — First enforcement of crypto market manipulation
South Korean authorities indicted a trader in the first pump-and-dump prosecution under the Virtual Asset User Protection Act, the new crypto law effective from July 2024.
Meanwhile, Upbit received a suspension notice for allegedly violating Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements in over 500,000 instances, prompting regulators to consider a ban on new user registrations.
Jan. 23 — Upbit, Bithumb compensate users after service outages during martial law
Upbit and rival exchange Bithumb announced plans to compensate users following service disruptions triggered by the surprise declaration of nationwide martial law on Dec. 3, 2024. The shocking move caused panic across financial and crypto markets, leading to a surge in traffic that overwhelmed local trading platforms.
Ex-President Yoon took his shot at martial law, which backfired and shaped South Korea’s 2025. Source: Kang Min Seok, Presidential Security Service South Korean crypto world finally opened to corporations
Feb. 13 — Charities and universities get first dibs on corporate crypto access
The FSC unveiled its long-awaited plan to allow corporate entities to open crypto trading accounts in phases by late 2025. The rollout will require businesses to use “real-name” accounts and comply with KYC and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. Charities and universities are first in line and will be allowed to sell their crypto donations starting in the first half of the year.
South Korea’s real-name financial transaction system, introduced in 1993, was designed to combat tax evasion and money laundering by requiring all bank accounts to be opened under verified legal names using national IDs.
Related: Market maker deals are quietly killing crypto projects
Crypto trading exploded in 2017, driven in part by anonymous accounts from businesses, foreigners and minors. Financial authorities responded by requiring crypto exchanges to partner with domestic banks and offer fiat services only through verified real-name accounts. To date, only five exchanges have met the requirements.
Since there was no regulatory framework for real-name corporate accounts, this policy effectively shut out both overseas users and domestic companies from trading on South Korean exchanges. The new roadmap aims to fix that by creating a formal structure for institutional participation under tighter compliance standards.
Feb. 21 — Alleged serial fraudster busted again
Police rearrested “Jon Bur Kim,” identified by the surname Park, for allegedly profiting 68 billion won (approximately $48 million) in a crypto scam involving the token Artube (ATT). He allegedly employed false advertising, pump-and-dump tactics and wash trading to manipulate the market.
This wasn’t Park’s first brush with the law. He was previously indicted in a 14-billion-won (around $10 million) token fraud case and was out on bail when he launched ATT.
Park flashes supercars on social media. Source: Jon Bur Kim Feb. 25 — Upbit operator Dunamu gets slapped
The nation’s Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) formally notified Dunamu, operator of Upbit, of regulatory action. The sanctions were tied to KYC compliance failures and dealings with unregistered foreign exchanges. The FIU issued a partial business suspension, restricting Upbit from processing new customers’ deposits and withdrawals for three months.
Feb. 27 — Crypto crime force formalized
South Korean prosecutors formally launched the Virtual Asset Crime Joint Investigation Division, following a year and seven months as a temporary operation. As a non-permanent unit from July 2023, the task force indicted 74 individuals, secured 25 arrests, and recovered over 700 billion won (around $490 million) in illicit gains. The 30-person task force includes prosecutors, regulatory staff and specialists.
Feb. 28 — Upbit operator Dunamu files lawsuit to overturn business sanctions
Dunamu said it filed a lawsuit against the FIU to challenge the sanctions imposed on the exchange.
Bitcoin ETF next on checklist for South Korean crypto space
March 5 — Reconsidering Bitcoin ETF ban
The FSC started reviewing legal pathways to allow Bitcoin (BTC) spot exchange-traded funds (ETFs), citing Japan’s evolving regulatory approach as a potential model. This marks a notable shift from South Korea’s previous opposition to crypto-based ETFs.
The Capital Markets Act does not recognize cryptocurrencies as eligible underlying assets for ETFs. However, in 2024, lobbying efforts from major domestic brokerages intensified amid rising client demand, especially after spot Bitcoin ETFs were approved in the US.
While the review remains in its early stages, regulators are no longer dismissing the possibility outright.
March 21 — Crackdown on unregistered exchanges begins
The FIU compiled a list of illegal foreign exchanges and moved to block access via app stores and ISPs. Additionally, the agency warned of criminal penalties for trading platforms operating without a license.
March 26 — 17 exchange apps blocked (including KuCoin and MEXC)
Google Play removed 17 unlicensed crypto exchange apps in South Korea at the request of regulators. The FIU said it is also working with Apple to block unauthorized crypto platforms.
There are 22 unregistered overseas exchanges on the regulators’ radar, and 17 have been banned from the Google Play store. Source: FSC March 27 — Upbit scores three-month break
A South Korean court temporarily lifted the Feb. 25 partial business suspension imposed on crypto exchange Upbit by the FIU. The court’s decision allows Upbit to resume serving new users while the case is under review.
South Korean crypto expected to go from crackdown in Q1 to campaign trail in Q2
As March ended, more than 16 million investors — roughly a third of South Korea’s population — held crypto accounts, surpassing the 14.1 million domestic stock traders. But that surge in adoption came as trading activity cooled. Upbit, the country’s dominant exchange, saw volumes fall by 34%, dropping from $561.9 billion in Q4 2024 to $371 billion in Q1 2025, according to CoinGecko.
By mid-April, the crackdown was still gaining steam. Apple followed Google’s lead in removing offshore exchange apps from its store, while prosecutors filed yet another round of market manipulation charges.
South Korea’s crypto industry is now contending with tighter rules, rising institutional expectations and a government no longer content to watch from the sidelines.
All this unfolds ahead of an early presidential election in June, following Yoon’s impeachment. Crypto played a visible role in Yoon’s successful 2022 presidential election campaign and is expected to remain a key issue with voters.
One candidate in the upcoming election, former prosecutor Hong Joon-pyo of the People Power Party, recently pledged to overhaul crypto regulations in line with the pro-industry stance of the Trump administration, local media reported. Despite the pledge, Hong’s understanding of the technology came into question as he admitted to not knowing what a central bank digital currency is.
Magazine: Uni students crypto ‘grooming’ scandal, 67K scammed by fake women: Asia Express

How to use a crypto hardware wallet in 2025
TL;DR
This guide shows you how to set up and use a crypto hardware wallet, using the Trezor Safe 3 as an example. You’ll learn to safely store Bitcoin, Ethereum and other assets offline, with clear steps for wallet setup, seed phrase backup, PIN protection and secure transaction signing. The article also explains how to connect your hardware wallet to MetaMask for use with DeFi platforms and NFTs – all while keeping your private keys offline. Whether you’re comparing the best hardware wallets in 2025 or need a crypto wallet tutorial for receiving and sending funds, this guide has you covered with actionable tips and best practices for long-term cold storage security.
If you’re ready to take crypto wallet security seriously, using a hardware wallet is one of the best steps you can take.
You may already be aware of its advantages over a software wallet: keeping your private keys offline, minimizing exposure to malware and giving you full ownership of your crypto assets. Maybe you’ve even picked out your device.
The good news? While there are several options out there, from Ledger to Trezor to newer multichain hardware wallets, the basic experience is similar. This hardware wallet setup guide will walk you through unboxing, verifying the device, securing your PIN and backing up your seed phrase.
For illustration purposes, this article uses the Trezor Safe 3, an ideal device for beginners but powerful enough for advanced users. It’s also a great choice if you want to use a hardware wallet for DeFi or connect your hardware wallet to MetaMask.
Let’s get into it.
Unboxing your crypto cold wallet
Before you begin setup, here’s what comes with a typical hardware wallet, in this case, the Trezor Safe 3. This applies to most of the best hardware wallets in 2025.
What’s in the box:
First steps: Inspect and verify
Before plugging anything in, check for:
-
Sealed, undamaged packaging.
-
Intact holographic sticker over the USB port.
This ensures your device hasn’t been tampered with, a crucial crypto wallet security tip. Newer devices (post-April 2024) have upgraded seals for added air-gapped security.
If anything looks suspicious, contact Trezor support.
Power it up
Peel the sticker and connect via USB — the Safe 3 powers on automatically, and no battery or power button is needed.
You’ll notice a small screen and two physical buttons. These are how you’ll confirm actions, approve transactions and manage your crypto.
Let’s begin the setup.
Hardware wallet setup: Trezor Safe 3
Getting started takes about 10–15 minutes. For this crypto hardware wallet tutorial, just have your computer ready and a pen handy. You’ll soon need to write down something very important.
Step 1: Download Trezor Suite
Go to the official Trezor site and download the Trezor Suite app. It’s available on Windows, macOS, Linux and via web browser.
Open it, plug in your device and follow the prompts. Click “Set up my Trezor.”
Step 2: Install firmware
Your device may not come with firmware pre-installed. Click “Install Firmware.” This is part of the crypto wallet recovery process and ensures a secure, clean slate.
Step 3: Verify device authenticity
Click “Let’s check your device” in Trezor Suite. Press the right button on your Safe 3 to authenticate. You’ll see a message confirming the device is verified.
Step 4: Quick tutorial
The device might walk you through button usage. Just follow along, it’s a one-time setup.
Step 5: Create a new wallet
You’ll see two options:
-
Create new wallet (choose this if it’s your first time).
-
Recover wallet (for restoring, using your seed phrase).
Step 6: Backup method
You’ll choose between:
-
Standard seed backup (easiest and most common).
-
Shamir backup (advanced; splits the seed into parts).
Stick with standard, unless you’re sure you know what you’re doing.
Step 7: Confirm on device
Use the buttons to confirm your backup method and agree to terms. Press “Create wallet” to proceed.
Step 8: Write down your recovery seed
This is the heart of your cold storage for crypto. The device will generate a random list of 12, 20 or 24 words, your recovery seed.
Trezor will remind you not to take photos or digital notes of the seed. Write it down on the provided card and store your crypto seed phrase safely. This is critical for future recovery.
Step 9: Confirm the seed
You’ll be tested on a few of the words (e.g., “What’s word #5?”). Select the correct ones using the buttons. Once confirmed, your backup is complete.
Pro tip: Make a second copy of your seed and store it in a different secure location. This adds an extra layer of protection.
Step 10: Set up a PIN
Now, create your hardware wallet PIN. In Trezor Suite, click “Set PIN.” The device will prompt you with a randomized layout. Use the buttons to choose your digits.
PINs can be up to 50 digits long. Choose something memorable, but not obvious. If forgotten, you’ll need to wipe the wallet and recover with the seed phrase.
Step 11: Enable coins and final setup
You’ll now choose which coins to enable, Bitcoin (BTC), Ether (ETH) and more. This step also prepares your wallet for use with DApps or storing Bitcoin in a hardware wallet.
After clicking “Complete Setup,” you can name your device or customize the home screen. Then hit “Access Suite” to open your dashboard.
If you’ve been following along on your own device, you’ve just completed your first hardware wallet setup and taken a major step toward storing crypto safely!
Receiving crypto with a hardware wallet
Once your device is set up, you’re ready to store crypto safely by receiving funds into your wallet. Here’s how to accept crypto securely with your Trezor hardware wallet.
1. Open the correct account
In Trezor Suite, choose the account for the crypto you want to receive (e.g., Bitcoin #1 or Ether #1). Click the “Receive” tab to generate a crypto cold wallet address.
2. Show and confirm the address
Click “Show full address” in the app. Your Trezor will display the full address on its screen. Always confirm the address on the hardware wallet itself, not just in your browser. This ensures it hasn’t been altered by malware on your computer (a standard crypto wallet security tip).
3. Use the address
Copy the address or scan the QR code to send crypto. Your Trezor doesn’t need to stay connected; the blockchain will receive the funds and update your balance next time you plug the wallet in.
Pro tips for safe receiving:
-
Confirm addresses on your device, not just your screen.
-
Use a fresh address each time for added privacy (Trezor Suite supports this).
-
If the address doesn’t match between your wallet and app, stop immediately.
Sending crypto from a hardware wallet
Sending crypto with a hardware wallet means your private key stays offline, even while broadcasting a transaction. Here’s how to do it securely:
1. Select the correct account
In the Trezor Suite, go to the account holding the asset you want to send. Click “Send.”
2. Fill in transaction details
Enter the recipient’s wallet address and the amount to send. You can also toggle to fiat view if needed. Double-check the recipient address to avoid mistakes.
3. Choose a Fee
-
For Bitcoin, you can select from fee levels: Low, Standard or High.
-
For Ether or ERC-20 tokens, Trezor Suite estimates gas fees automatically.
4. Confirm on the device
Click “Review & Send.” Your Trezor will display the transaction details:
-
Destination address.
-
Amount.
-
Network fee.
Only approve the transaction if everything checks out. This is how you protect yourself from clipboard malware.
5. Done, signed transaction is now sent!
Your signed transaction has now been sent, with zero exposure of your private key. You’ll see the confirmation in your history.
More pro tips:
-
If your Trezor asks to sign a transaction you didn’t initiate, cancel immediately.
-
Make sure your ETH balance is sufficient to cover gas for token transfers.
-
For advanced users: Trezor also supports air-gapped security setups using microSD backups.
Using a hardware wallet with MetaMask and DApps
Want to use your hardware wallet for DeFi or NFTs while keeping your keys secure? Trezor Safe 3 integrates seamlessly with MetaMask, making it easy to use DApps and sign transactions safely.
1. Connect Trezor to MetaMask
Open MetaMask in your browser. Click your account icon and choose “Connect Hardware Wallet.” Select Trezor when prompted.
2. Plug in your Trezor
If not already connected, plug in the device. MetaMask may prompt you to install Trezor Bridge, a utility that enables communication with the wallet.
You’ll be asked to approve the reading of your public key from the hardware wallet. This is safe and doesn’t reveal private keys.
3. Select a wallet address
MetaMask will list your Trezor-linked Ethereum addresses. Choose one (e.g., Ethereum #1) and click “Unlock.” The wallet will now appear in MetaMask, marked as a hardware wallet.
How it works
From now on, every time you make a transaction, whether it’s swapping tokens on Uniswap or minting an NFT, you will:
-
Initiate the transaction in MetaMask.
-
See the details appear on your Trezor screen.
-
Physically confirm the transaction using your device buttons.
This flow ensures that even if your browser is compromised, the final transaction approval happens on your trusted hardware wallet.
Final safety tip: Your hardware wallet screen is the most trustworthy place to verify transaction details. Never rely solely on what you see in the browser.
Why hardware wallets matter in 2025
Whether you’re storing Bitcoin, using DeFi protocols or exploring NFTs, hardware wallets remain the gold standard for crypto security. With cold storage for crypto, recovery tools like seed phrases and integration with platforms like MetaMask offer powerful protection with ease of use.
If the Trezor Safe 3 feels like a good fit, it’s available at a discount via the provided link, a smart first step into secure, self-custodied crypto.
Still weighing your options? Explore the updated 2025 guide to the best hardware wallets. It covers Ledger setup, Trezor guides, and more, including advanced models for multichain use, long-term backups and offline storage.
Disclaimer. Cointelegraph does not endorse any content or product on this page. While we have striven to provide all the essential information available in this article, please note that it contains affiliate links. Readers are encouraged to conduct their own research before making any decisions related to the company. This article should not be considered investment advice.
-
How Mantra’s OM token collapsed in 24 hours of chaos
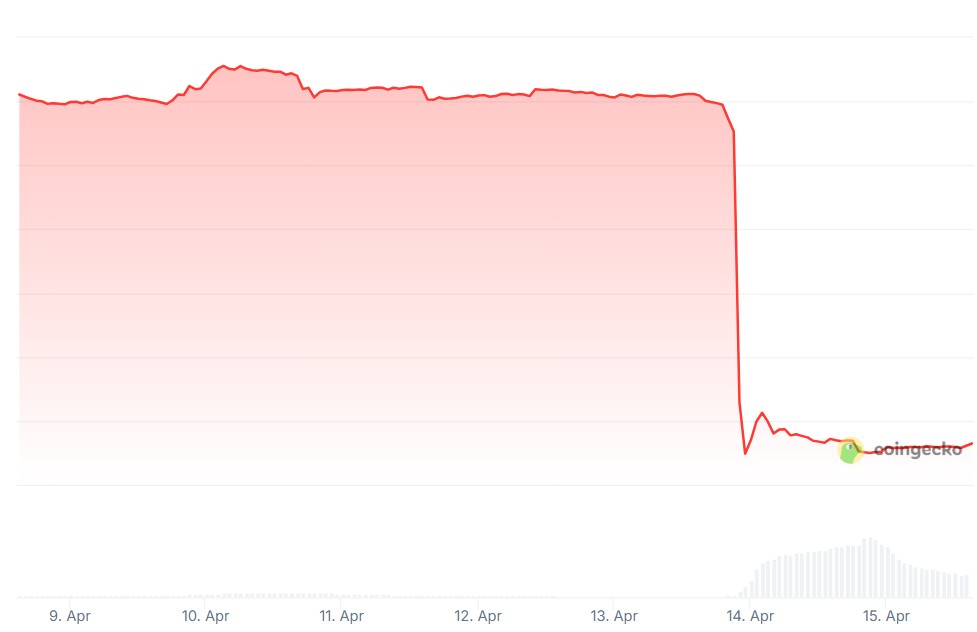
Mantra’s OM token collapsed by more than 90% overnight, and the crypto world can’t agree on why. On April 13, OM’s price plummeted from over $6 to below $0.50, wiping out more than $5 billion in market cap and triggering widespread panic across the crypto industry.
The sudden crash drew comparisons to Terra’s LUNA implosion as traders scrambled for answers. Unverified rumors of insider dumping, forced liquidations, mislabeled wallets and exchange manipulation quickly spread — but Mantra insists it was caught in the middle.
Mantra had built a strong position in the real-world asset tokenization narrative heading into April 13, backed by a $1-billion deal to tokenize Dubai-based Damac Group’s real estate and data centers. It secured a Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) license in Dubai and launched a $108-million ecosystem fund with support from heavyweights such as Laser Digital, Shorooq, Amber Group and Brevan Howard Digital. In February 2025, the OM token hit an all-time high of nearly $9.
But on April 13, that momentum was violently interrupted. The hours that followed painted a messy picture of token transfers, insider speculation and shifting blame. Here’s a detailed look at how the OM collapse played out.
24 hours of the Mantra OM fiasco
April 13 (16:00–18:00 UTC)
Mantra’s OM token was trading sideways throughout the day. It dropped from $6.14 to $5.52 during this two-hour window.
April 13 (18:00–20:00 UTC)
The token suddenly fell to $1.38 in the first hour, then to as low as $0.52 in the next — losing over 90% of its value in a single day. Social media erupted with theories, including a rug pull, insider dumping, forced liquidation or exchange manipulation.
Mantra’s OM loses over 90% of its value in just a few hours. Source: CoinGecko April 13 (20:00–22:00 UTC)
Early speculation surrounded a rug pull, sparked by a screenshot of a deleted Telegram channel. This was later debunked, as the deleted group was not Matra’s official channel. Cointelegraph has confirmed that the project’s Telegram is active at the time of writing.
Mantra shared its first statement on X, but the brief update was met with immediate backlash from the community.
Mantra says OM’s crash was due to “reckless liquidations.” Source: Mantra/Exy April 13 (22:00–00:00 UTC)
Mantra co-founder and CEO John Patrick Mullin posted a more detailed statement on X, claiming OM’s market action was triggered by “reckless forced closures initiated by centralized exchanges on OM account holders.”
“The timing and depth of the crash suggest that a very sudden closure of account positions was initiated without sufficient warning or notice,” Mullin said.
“That this happened during low-liquidity hours on a Sunday evening UTC (early morning Asia time) points to a degree of negligence at best, or possibly intentional market positioning taken by centralized exchanges.”
Related: Atkins becomes next SEC chair: What’s next for the crypto industry
April 14 (00:00–02:00 UTC)
In the days leading up to the crash, at least 17 wallets had deposited a total of 43.6 million OM (worth $227 million) into Binance and OKX, according to blockchain tracker Lookonchain.
Two of these wallets were labeled as belonging to Laser Digital, a strategic Mantra investor, by blockchain data platform Arkham Intelligence. The label triggered further speculation and allegations against Laser Digital. At the time of writing, the accuracy of Arkham’s labels has not been confirmed, and the platform has not responded to Cointelegraph’s request to clarify.
Laser Digital is still tagged on Arkham’s platform. Source: Arkham Intelligence Meanwhile, Mullin replied to community questions under his X post, suggesting internal findings pointed to one exchange as the main cause of the collapse while stating that it was not Binance.
April 14 (02:00–05:00 UTC)
Both Binance and OKX responded to the situation. Binance said, “Binance is aware that $OM, the native token of MANTRA, has experienced significant price volatility. Our initial findings indicate that the developments over the past day are a result of cross-exchange liquidations.”
OKX CEO Star Xu posted on X, “It’s a big scandal to the whole crypto industry. All of the onchain unlock and deposit data is public, all major exchanges’ collateral and liquidation data can be investigated. OKX will make all of the reports ready!”
OKX stated, “Following the incident, we have conducted investigations and identified major changes to the MANTRA token’s tokenomics model since Oct 2024, based on both publicly available on-chain data and internal exchange data.
“Our investigation also uncovered that several on-chain addresses have been executing potentially coordinated large-scale deposits and withdrawals across various centralized exchanges since Mar 2025.”
April 14 (05:00–12:00 UTC)
Laser Digital denied ownership of the wallets tagged by Arkham and reported by Lookonchain, calling them mislabeled.
“We want to be absolutely clear: Laser has not deposited any OM tokens to OKX. The wallets being referenced are not Laser wallets,” the company said on X, sharing three token addresses to support its claim that no sales had occurred.
Lookonchain also identified another wallet using Arkham data that had remained dormant for a year before becoming active just hours before the crash. The wallet was labeled as belonging to Shane Shin, a founding partner of Shorooq Partners, and received 2 million OM shortly before the collapse.
Source: Lookonchain/Shae Shin April 14 (12:00–13:00 UTC)
Mullin joined Cointelegraph’s Chain Reaction show and denied reports that key Mantra investors dumped OM before the collapse. He dismissed allegations that the team controlled 90% of the supply.
“I think it’s baseless. We posted a community transparency report last week, and it shows all the different wallets,” Mullin said, noting the dual-token setup across Ethereum and the Mantra mainnet. Additionally, he reassured users that OM token recovery is the team’s primary concern.
“We’re still in the early stages of putting together this plan for a potential buyback of tokens,” he said.
Related: The whale, the hack and the psychological earthquake that hit HEX
April 14 (13:00–16:00 UTC)
More theories started emerging. Onchain Bureau claimed market makers at FalconX were responsible for the price crash. They blamed it on the loan option model — a service allowing market makers to borrow tokens and execute guaranteed purchases at contract expiry.
“Instead of paying the market maker with a monthly retainer fee, they had a contract signed saying that they would be able to enforce a buy of, for example, 1M tokens at $1 by contract expiry. Clearly, when the contract expired, they enforced the contract and made their bags,” Onchain Bureau said in a now-deleted X post.
Shortly afterward, Onchain Bureau followed up, saying FalconX had reached out and denied being Mantra’s market maker. Mullin also responded to the post, stating that FalconX was not the project’s market maker. He described them instead as a trading partner.
Meanwhile, crypto detective ZachXBT weighed in, claiming that individuals linked to Reef Finance had allegedly been seeking massive OM-backed loans in the days leading up to the crash.
Source: ZachXBT What we know of the OM crash
Several theories have been thrown around. Initial fears ranged from a rug pull to insider trading, which Mantra has denied in several instances by sharing wallet addresses. The team has responded to online comments and media inquiries to assure that they haven’t run away.
Mantra has also denied that the price collapse was a result of an expiring deal with market maker FalconX. Some fingers were pointed toward Laser Digital, which said it is a result of mislabeling at Arkham Intelligence.
Arkham Intelligence has not responded to Cointelegraph’s request to clarify its labels. However, the Laser Digital tags on Arkham are a low-confidence prediction made by an AI model, not a verified entity with a blue checkmark.
Magenta-colored labels on Arkham Intelligence are low-confidence AI predictions, not verified wallets. Source: Arkham Intelligence In the days following the OM crash, Mullin stated that he would burn all of his team’s tokens. He later said that he would start by putting his own allocation on the line.
Mullin announced that Mantra would publish a post-mortem and followed with a “statement of events” on April 16. The team reiterated that no project-led token sales occurred and that all team allocations remain locked. The statement doubled down on Mantra’s plan to introduce a token buyback and burn program but lacked new information on the cause of the crash.
Mullin told Cointelegraph that Mantra has tapped an unnamed blockchain analyst to investigate the underlying cause of the crash, though details remain confidential at this time.
Magazine: Memecoin degeneracy is funding groundbreaking anti-aging research
How Meta’s antitrust case could dampen AI development
Meta, the parent company of Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp and Messenger, is facing antitrust proceedings that could limit its ability to develop AI amid a field of competitors.
First filed in 2021, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) alleges that Meta’s strategy of absorbing firms — rather than competing with them — violates antitrust laws. If the court rules against Meta, it could be forced to spin out its various messenger services and social media sites into independent companies.
The loss of its stable of social media companies could harm Facebook’s competitiveness not only in the social media industry but also in its ability to train and develop its proprietary Llama AI models with data from those sites.
The trial could take anywhere from a couple of months to a year, but the outcome will have lasting consequences on Meta’s standing in the AI race.
Meta’s antitrust case and its effect on AI
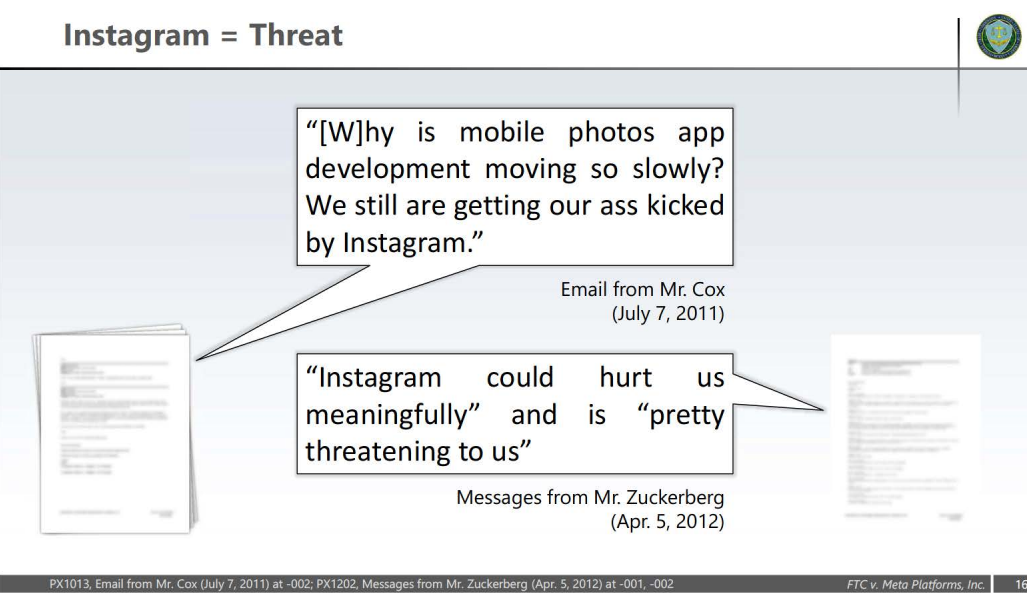
The FTC first opened its complaint against Meta in 2020 when the firm was still operating as Facebook. The agency’s amended complaint a year later alleges that Meta (then Facebook) used an illegal “buy-or-bury” scheme on more creative competitors after its “failed attempts to develop innovative mobile features for its network.” This resulted in a monopoly of the “friends and family” social media market.
Meta founder and CEO Mark Zuckerberg had the chance to address these allegations on April 14, the first day of the official FTC v. Meta trial. He testified that only 20% of user content on Facebook and some 10% on Instagram was generated by users’ friends. The nature of social media has changed, Zuckerberg claimed.
“People just kept on engaging with more and more stuff that wasn’t what their friends were doing,” he said — meaning that the nature of Meta’s social media holdings was sufficiently diverse.
The FTC alleges that Meta identified potential threat competitors and bought them up. Source: FTC At the time of the FTC’s initial complaint, Meta called the allegations “revisionist history,” a claim it repeated on April 13 when it stated the agency was “ignoring reality.” The company has argued that the purchases of Instagram and WhatsApp have benefited users and that competition has appeared in the form of YouTube and TikTok.
If the District of Columbia Circuit Court rules against Meta, the global social media giant will be forced to unwind these services into independent firms. Jasmine Enberg, vice president and principal analyst at eMarketer, told the Los Angeles Times that such a ruling could cost Meta its competitive edge in the social media market.
“Instagram really is its biggest growth driver, in the sense that it has been picking up the slack for Facebook for a long time, especially on the user front when it comes to young people,” said Enberg. “Facebook hasn’t been where the cool college kids hang out for a long time.”
Such a ruling would also affect the pool of data from which Meta can draw to train its AI models. In July 2024, Meta halted the rollout of AI models in the European Union, citing “regulatory uncertainty.”
The pause came after privacy advocacy group None of Your Business filed complaints in 11 European countries against Meta’s use of public data from its platforms to train its AI models. The Irish Data Protection Commission subsequently ordered a pause on the practice until it could conduct a review.
Related: Meta’s Llama 4 puts US back in lead to ‘win the AI race’ — David Sacks
On April 14, Meta got the go-ahead to use public data — i.e., posts and comments from adult users across all of its platforms — to train the model. If these firms dissolved into separate companies, with their own organizational structures and data protection policies and practices, Meta would be cut off from an ocean of data and human communication with which its AI could be improved.
Andrew Rossow, a cyberspace attorney with Minc Law and CEO of AR Media Consulting, told Cointelegraph that in such an event, “companies would most likely control their own user data, and Meta would be restricted from using it unless new data-sharing agreements were negotiated, which would be subject to regulatory scrutiny and user/consumer privacy laws.”
However, Rossow noted that it wouldn’t be a total loss for Meta. Zuckerberg’s firm would retain the wealth of data from Facebook and Messenger. It could continue to use “opt-in” data from consumers who allow their posts to be used for AI training, and it could also employ synthetic data sets as well as third-party and open data.
Meta, the AI race and data protections
The race to unseat OpenAI and its ChatGPT model from AI dominance has grown more competitive in the last year as DeepSeek joined the fray and Meta launched the fourth iteration of its open-source Llama model.
In addition to training new models, major AI development firms are investing billions in new data centers to accommodate new iterations. In January 2025, Meta announced the construction of a 2-gigawatt data center with more than 1.3 million Nvidia AI graphics processing units.
Zuckerberg wrote in a post on Threads, “This will be a defining year for AI. In 2025, I expect Meta AI will be the leading assistant serving more than 1 billion people […] To power this, Meta is building a 2GW+ datacenter that is so large it would cover a significant part of Manhattan.”
Illustration of the data map coverage. Source: Mark Zuckerberg His announcement followed the $500-billion Stargate project, which would see massive investment in AI development led by OpenAI and SoftBank, with Microsoft and Oracle as equity partners.
Related: Trump announces $500B AI infrastructure venture ‘Stargate’
Amid this competition, AI firms are looking for broader and more varied sources of data to train their AI models — and have turned to dubious practices in order to get the data they need. In order to stay competitive with OpenAI when developing its Llama 3 model, Meta harvested thousands of pirated books from the site LibGen. According to court documents in a case pending against Meta, Llama developers harvested data from pirated books because licensing them from sources like Scribd seemed “unreasonably expensive.”
Time was another perceived motivator for using pirated works. “They take like 4+ weeks to deliver data,” one engineer wrote about services through which they could purchase book licenses.
The practice is not limited to Meta. OpenAI has also been accused of mining data from pirated work hosted on LibGen.
Rossow suggested that, “to ensure lasting impact — beyond short-term profit,” Meta would do well to “prioritize investment in advanced data collection, rigorous auditing and the implementation of privacy-preserving and encryption-based technologies.”
By focusing on transparency and responsible practices, “Meta can continue to genuinely advance AI capabilities, rebuild and nurture long-term user trust, and adapt to evolving legal and ethical standards, regardless of changes to its platform portfolio.”
What a ruling for the FTC would mean
Litigation is now hitting tech firms from all sides as they face allegations of privacy violations, copyright law infringement and stifling competition. Major cases like those facing Google, Amazon and Meta that have yet to play out will decide how and whether these firms can proceed as they have, defining the guardrails for AI development as well.
Rossow said that the current antitrust case against Meta could decide how courts interpret antitrust law for tech firms, spanning tech mergers, data usage and market competition. It would also signal that courts are “willing to break up tech conglomerates” when issues of smothering competition are involved, while at the same time, “taking current precedent a step further in harmonizing it with the laws of cyberspace.”
Magazine: Memecoin degeneracy is funding groundbreaking anti-aging research

Cash-based crypto can enable financial inclusion for billions

Opinion by: Alexander Guseff, founder and CEO of Tectum
Crypto companies have spent years pushing digital wallets and exchange apps, convinced they’ll bring financial inclusion to the world. Here’s the reality: 1.4 billion people remain unbanked, and crypto adoption has barely exceeded 8%. For all the talk about decentralization and accessibility, the industry continues to overlook the billions of people who rely on cash for their daily lives.
In developing economies of Africa, South Asia and Latin America, cash is not just dominant — it’s essential. Banking services are sparse, smartphone penetration is low, and digital literacy remains a hurdle. Expecting these populations to onboard through a process designed for tech-savvy users with internet access is unrealistic.
Yet whenever offline crypto solutions have been tested, adoption has jumped. The message is clear: People are willing to use crypto but need a way to access it that fits their reality.
The global reality of cash dependence
Despite assumptions that digital finance will eventually replace cash, that’s not what the numbers show. Take Romania. Notably, 76% of transactions there are still cash-based, yet crypto adoption has hit 14%. In Morocco, cash remains king despite digital payment growth, yet 16% of the population has found a way to use crypto — even though it’s officially banned.
Then there’s Egypt, where approximately 72% of payments rely on cash, but crypto adoption sits at around 3%, primarily due to limited digital infrastructure. Even in India, where crypto enthusiasm runs high, 63% of transactions still happen in cash.
Across these markets, the pattern is clear: People want to use crypto, but the industry isn’t giving them a practical way to integrate it into their everyday transactions.
Crypto’s real problem
The barriers to crypto adoption go far beyond technology. Government regulations, economic conditions and local financial habits all play a role.
Crypto’s biggest flaw isn’t a lack of demand. It’s the assumption that digital wallets and banking apps are the only viable entry points. That thinking ignores billions of people who still operate in cash-driven economies.
A more practical approach
Instead of forcing a digital-only model onto cash-heavy regions, crypto should adapt. Blockchain-linked physical banknotes, QR-coded vouchers and SMS-based transfers could bring crypto into the real economy in a way that makes sense for people who already use cash.
Recent: Stop making crypto complex
The idea isn’t as radical as it sounds. Africa’s M-Pesa, which has over 66.2 million active users, operates on a simple agent-based model that lets people exchange cash for digital value without needing a bank account. The same approach could work for crypto, enabling users to trade blockchain-linked cash notes at local vendors.
It’s already happening in small pockets. Machankura, for example, enables Bitcoin transactions via basic mobile networks, attracting over 13,600 users in Africa. In a region where nearly all digital payments rely on simple mobile codes rather than smartphone apps, solutions like this are far more viable than pushing another exchange-based onboarding process.
Security concerns will always come up with physical assets, but trained agents and proper oversight can mitigate risks. More importantly, that’s a solvable problem — excluding billions of people from the financial system isn’t.
The digital purists get it wrong
Many in the crypto space dismiss paper-based solutions as outdated. The idea that everything must be digital ignores how financial systems evolve. People need time to transition and systems that fit their current way of life.
CoinText, an SMS-based crypto transfer service, spread to 50 countries before it shut down — not because the idea didn’t work, but because the industry wasn’t ready to support it.
The same rigid thinking that dismissed SMS transfers is now preventing adoption in cash-heavy economies. A new service called Text BSV has emerged, enabling seamless peer-to-peer (P2P) payments of satoshis via SMS — no app downloads, registrations or prior knowledge of Bitcoin (BTC) is required. It works on any phone, even non-smartphones.
If crypto adoption remains stalled at 8%, it won’t be because people don’t want it. It’ll be because the industry insisted on an approach that doesn’t work for most of the world.
A $50-billion opportunity
The financial upside of integrating crypto into cash economies is enormous. Similar markets could follow if Romania, with a 76% cash reliance, can reach 14% adoption. That translates into a $50-billion opportunity globally as crypto enters economies where trillions of dollars move in informal cash transactions every year.
A network of cash-to-crypto agents could generate $10 billion in revenue by 2030, mirroring the success of mobile money platforms like M-Pesa. Even crypto exchanges would benefit from tapping into these underserved markets, bridging the gap between digital and cash economies.
Regulators may hesitate at paper-based crypto owing to transparency concerns, but financial inclusion at this scale is hard to ignore. If governments see a potential $50 billion in new economic activity, they’re more likely to work toward solutions rather than block progress.
Cash meets crypto
Crypto was supposed to revolutionize financial access, but it remains out of reach for billions of people. Expecting these communities to abandon cash entirely and jump straight into digital wallets is unrealistic and a bad strategy
The solution isn’t to wait for these economies to modernize. It’s to meet people where they are. That means experimenting with cash-compatible solutions, partnering with telecom providers, and rolling out agent-based models that let people use crypto in a way that feels familiar.
The current adoption stall will become permanent if the industry doesn’t make these changes. Instead of a step backward, paper-based crypto could be the bridge that finally connects billions of people to the future of finance.
Opinion by: Alexander Guseff, founder and CEO of Tectum.
This article is for general information purposes and is not intended to be and should not be taken as legal or investment advice. The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed here are the author’s alone and do not necessarily reflect or represent the views and opinions of Cointelegraph.

5 reasons why FARTCOIN is rising faster than everything else
Fartcoin (FARTCOIN), a Solana-based memecoin launched in October 2024, has soared over 370% from its yearly low, outperforming Bitcoin (BTC) even as global trade tensions weigh on broader risk assets.
These are the five key reasons why FARTCOIN is rising faster than top cryptocurrencies.
FARTCOIN/USDT vs. BTC/USD 30-day price chart comparison. Source: TradingView PEPE boom similarities fuel FARTCOIN hype
FARTCOIN’s recent surge mirrors the early stages of Pepe’s (PEPE) meteoric rise.
In 2023, PEPE launched with a rapid ascent to a $1.8 billion market cap before crashing down to $255 million, according to the PEPE/WETH weekly chart.
From there, it bottomed out, consolidated, and then entered a second, even more powerful rally that carried it beyond a $4 billion valuation.
PEPE/WETH weekly performance chart. Source: DEX Screener/MacroCRG The euphoric pump, harsh correction, and quiet accumulation phase look similar to what FARTCOIN is showing now.
The Solana memecoin peaked near $2.4 billion earlier this year before undergoing a brutal drawdown. Its valuation dropped to around $365 million, forming a rounded bottom pattern.
FARTCOIN/SOL weekly price chart. Source: DEX Screener/MarcoCRG From there, FARTCOIN has steadily climbed back, reaching about $949 million this week. That is strikingly similar to PEPE’s post-hype accumulation phase in 2023.
“I genuinely think there’s a chance Fartcoin repeats the PEPE playbook and pulls some crazy multiples from here,” wrote market analyst MacroCRG, citing the PEPE memecoin fractal.
Fartcoin’s social media hype spikes 500%
FARTCOIN appears to be riding a fresh wave of speculative mania, with social media metrics revealing a sharp rise in online activity.
FARTCOIN’s social volume (orange line) surged by nearly 500% in early April, preceding its 100%-plus gains in the month, according to data resource LunarCrush.
As of April 17, the engagement had cooled slightly, albeit remaining elevated at 177% above baseline.
FARTCOIN social volume, dominance and contributors 30-day chart. Source: LunarCrush Social dominance (purple) and social contributors (blue) have both trended higher, up 162% and 136%, respectively.
Rising social media activity in crypto markets often correlates with increased speculative interest, particularly in meme-driven assets.
While not a guaranteed indicator of future price action, a surge in social metrics can reflect growing community engagement and heightened visibility, factors that are now coinciding with sharp moves in FARTCOIN.
Fartcoin OI jumps over 500%
Fartcoin’s open interest (OI) in the futures market has jumped by around 504% so far in 2025, according to data resource CoinGlass. A rising OI indicates a massive influx of capital and attention from traders.
FARTCOIN futures open interest. Source: CoinGlass In contrast, Bitcoin’s OI has declined by 10.5% during the same period, reflecting reduced speculative interest in the leading crypto asset.
Adding to the bullish case, FARTCOIN’s funding rates have remained largely positive throughout April, showing that more traders are betting on the price going up than down.
FARTCOIN funding rates (8-hour). Source: CoinGlass Periods of negative funding rates in the FARTCOIN futures market have consistently aligned with disproportionately large short liquidations, highlighting the risks of betting against this popular memecoin.
A clear example occurred on April 9, when FARTCOIN’s eight-hour funding rate plunged to -0.023%, signaling a wave of bearish sentiment as traders aggressively shorted the token.
FARTCOIN funding rates and liquidation charts. Source: CoinGlass But in a classic short squeeze, FARTCOIN surged by nearly 50% the same day, triggering $9.16 million in short liquidations, compared to just $2.52 million in longs.
This stark imbalance underscores a growing pattern: When too many traders lean bearish, FARTCOIN often moves sharply against them.
As a result, short sellers appear to be treading carefully, as excessive pessimism has repeatedly backfired, turning negative funding into a setup for explosive upside moves.
Fartcoin is founderless
Fartcoin’s rise reflects more than just meme-fueled hype—it stems from a unique narrative that actively blends AI innovation with internet absurdity.
New Zealand-based AI researcher Andy Ayrey created an AI agent called the Terminal of Truth, which conceived Fartcoin as part of an experiment in merging artificial intelligence with blockchain humor.
Source: X This unusual origin story has caught the attention of traders looking to capitalize on the intersection of AI and crypto, positioning Fartcoin as more than just a typical memecoin.
“Unlike most AI plays, it lives free of the execution risks and technical complexity of infra tokens *and* free of the fatigue and noise around tokenized agents,” wrote analyst Ben in December 2024, adding:
“This simplicity coupled with absurdity is the perfect recipe for reflexivity: higher price = higher absurdity = higher attention = higher price.”
Fartcoin’s team continues to build its brand around viral internet culture, planning a Goatse-inspired film to further fuel engagement.
It pushes the absurdity even further by incorporating a digital fart sound into its “Gas Fee” system—turning transaction costs into a deliberately crude punchline that reinforces its meme-first identity.
Source: X In doing so, Fartcoin has leveraged novelty and narrative to attract speculative capital without relying on a roadmap, founder figure or utility.
This strategy possibly explains why it has continued to gain momentum while many other tokens stall.
Fartcoin price technicals hint at 100% gains next
FARTCOIN’s price rally also has strong technical backing.
The four-hour chart of FARTCOIN/USDT shows an inverse head-and-shoulders pattern, a classic bullish reversal signal that often marks the end of a downtrend and the beginning of a sustained upward move.
This formation includes a left shoulder formed in early February, a deeper head in mid-March, and a right shoulder in early April, all anchored around a horizontal neckline around $0.63.
FARTCOIN/USDT four-hour price chart. Source: TradingView The pattern confirmed its breakout on April 10 when FARTCOIN surged above the neckline with strong volume. Following the breakout, the price has held above key moving averages — the 50-EMA and 200-EMA — while consolidating just under the $0.90 level.
Based on the distance from the head to the neckline, the measured move projection points to an upside target near $1.96, up by over 100% compared to current price levels.
This breakout adds a layer of technical confirmation to the ongoing rally, supporting the view that FARTCOIN’s momentum is narrative-driven and structurally supported by bullish chart patterns.
This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision.

What is a VTuber, and how do you become one in 2025?
Key takeaways
-
A Vtuber is a real person behind a digital avatar, blending performance, storytelling, and creativity to connect with audiences through livestreams, games, podcasts, and more.
-
Becoming a VTuber involves designing a unique avatar (2D or 3D), using motion capture for animation, and leveraging software tools like Live2D, VSeeFace, and AI voice modifiers.
-
In 2025, VTubing success often starts with short-form mobile platforms like TikTok and YouTube Shorts. Cross-posting to Discord, X, or Twitch helps build community and drive monetization.
-
Aspiring VTubers should be aware of risks like burnout, privacy breaches, platform dependency, and unpredictable income.
Virtual YouTubers, or VTubers, have gained popularity in recent years. VTubers create content for their channels using computer-generated avatars.
Although VTubers are particularly popular in Japan and other Asian countries, the trend is slowly spreading across the world.
So, what exactly is a VTuber? How does VTubing work, and how can you become one in 2025?
This article explores what a VTuber is, the tools and software, and how to start VTubing in 2025.
What is a VTuber?
Have you ever scrolled Twitch or YouTube and stumbled upon a virtual anime-style character live streaming, playing games and chatting with viewers? That was a VTuber.
A VTuber is a digital content creator who uses a virtual avatar to produce videos or live content.
These avatars are often animated in real-time using motion tracking and face capture, creating an online personality. These avatars can look like anime characters, animals, robots or even abstract creatures.
However, behind every VTuber is a real person, using their voice, expressions and personality to bring the character to life.
But how does an avatar actually copy your movements?
Motion capture, or mocap, is the technology behind avatars that records a person’s movements using sensors to create realistic animations for virtual characters in games, movies or virtual reality. It converts real-world movement into digital 3D data for more lifelike animation.
Some VTubers are run by professional businesses or agencies, while others are single creators with their own background stories and hand-crafted avatars.
Whether they’re broadcasting games, selling merchandise, podcasting or just vibing with their audience, VTubers have established a space where technology meets creativity, and it’s growing day by day.
VTuber vs. traditional YouTube content creator
Aren’t VTubers just YouTubers with cool avatars? Well, not exactly. It all comes down to how they show up on screen. While traditional YouTubers appear as themselves, VTubers use animated avatars to represent their online persona, whether a space alien or a talking cat.
The core content and interaction with the audience might be similar. Still, VTubing often leans into storytelling, roleplay and unique esthetics to create a more immersive experience for their fans, making the methods and approaches differ.
Did you know? In 2024, the VTuber market was valued at $2.55 billion; by 2035, it is projected to reach $20.0 billion.
How VTubing works and what tools are needed
As more creators dive into VTubing, the preparation required has also evolved, with a greater emphasis on crafting recognizable and unique characters to stand out in a crowded space.
Below are the key aspects that make up the process of becoming a VTuber, ensuring your avatar captures attention and engages audiences.
Virtual avatar
The process of creating a VTuber avatar in 2025 begins with concept development that involves designing the avatar’s appearance, personality and backstory.
Once the concept is in place, you can move on to creating the 2D or 3D model using specialized software such as Live2D Cubism for 2D models and Blender, Viverse Avatar or Vroid Studio for 3D models.
Choosing between a 2D or 3D avatar depends on your desired level of detail and animation, with 2D offering a more stylized, simpler look and 3D allowing for more dynamic, lifelike movement and depth.
After designing the avatar, the next step is rigging, which involves adding bones and joints to enable movement. This process is done by using rigging software like Live2D or VUP for 2D and tools like VSeeFace for 3D models. These tools allow the virtual avatar to replicate the performer’s movements, making the character blink, talk and gesture in real-time.
To capture and animate the performer’s movements, many VTubers use face-tracking mocap software such as VTube Studio or VSeeFace to track facial expressions.
Livestreaming and content creation
The VTuber can start creating livestream content once the virtual avatar has been designed and animated.
Livestreaming on platforms like YouTube and Twitch and gaming streams can be realized using software like OBS Studio or Streamlabs OBS.
To edit pre-recorded videos, creators rely on software such as DaVinci Resolve or Adobe Premiere Pro. Additionally, voice changers like Voicemod or MagicVox can help modify the creator’s voice to match their avatar. Custom graphics and overlays can be created using tools like Photoshop or Canva.
Engaged audience
The power of the virtual avatar to have real-time conversations with the audience is a unique feature of VTubing. Building a credible brand is essential to becoming a successful VTuber, just like it is for other types of content creation. This means creating a unique character or identity for the virtual avatar and creating content that appeals to the intended audience.
How to become a VTuber in 2025
Besides the core aspects of VTubing covered above, there are a few more essentials to consider if you’re serious about starting VTubing in 2025.
-
Use AI or avatar builders: Tools like Inworld or Ready Player Me offer plug-and-play solutions with simple customization. These are ideal for beginners who want to skip drawing and rigging. AI can also help with real-time voice modulation, AI-powered NPCs, or “non-player characters,” for collabs and even AI-generated scripts. Some VTubers are blending AI sidekicks into their streams.
-
Customize stream setup: In 2025, customizing your VTuber stream setup entails incorporating stylish overlays, notifications, background music and chat widgets. Also, practicing your stream flow is essential to ensure smooth delivery of voice, emotive reactions and transitions.
-
VTubing on TikTok and mobile: Short-form VTuber content is booming, especially on TikTok and YouTube Shorts. Many new creators start on mobile-first platforms before moving to full streams. Creating and sharing videos on platforms such as TikTok, X or Discord is essential for cross-platform marketing to reach new audiences, move your fans across platforms, and attract potential brand partnerships for sponsorship and ads.
Did you know? Kuzuha from Nijisanji topped the 2024 view hours chart with over 40 million hours, retaining his position as a fan favorite for the second year in a row, according to Vstats, which compiles data from websites such as YouTube, Twitch and Soop.
VTubing trends of 2025
Due to developing technologies and shifting audience tastes, starting a VTuber career in 2025 means understanding the latest trends to stand out in an increasingly crowded industry.
Niche content
In 2025, standing out as a VTuber can also mean going niche. GFE or BFE, girlfriend or boyfriend experience, continue to lead the charge. These formats build one-sided emotional connections with fans who often become long-term supporters through monetizing exclusive content on platforms like Patreon.
Autonomous sensory meridian response (ASMR) content continues to thrive, though creators must now carefully navigate platform rules to avoid demonetization. This content is designed to trigger relaxing tingles through soft sounds and visuals. Gaming and “Let’s Play” content continue to be a cornerstone while being an oversaturated niche.
In the end, the most prominent VTubers in the competitive landscape of 2025 are those who establish a clear identity, respect boundaries, and provide consistent, emotionally resonating material.
2D esthetics
Anime-style VTubers remain fan favorites, but 2025 has brought an extra layer of polish. Expect hyper-stylized 2D models with dynamic lighting, soft shading and intricate accessories. Subtle breathing, animated eyes and natural motion physics are raising the bar for Live2D designs.
Focus on culture and uniqueness
Avatar localization and distinctiveness extend beyond language; it entails modifying features, content and tactics to conform to regional norms, cultural preferences and local regulations. Platforms may increase user engagement by creating a feeling of community and relevance by customizing themselves for particular geographic areas.
Decentralized identities and NFTs
Some VTubers use blockchain to secure their avatars and sell collectibles such as non-fungible tokens (NFTs), helping monetize the avatars.
Risks of becoming a VTuber in 2025
While the VTuber space continues to grow rapidly in 2025 — with better tools, bigger audiences and even corporate sponsorships — aspiring creators should be aware of the risks involved.
Here are key challenges to consider before jumping in:
-
Burnout and creative fatigue: VTubing often requires constant content creation, livestreaming and staying in character, which can quickly lead to exhaustion without proper balance or breaks.
-
Privacy and doxxing threats: While VTubers use avatars to remain anonymous, popular creators are still at risk of having their real identities exposed, especially in toxic or competitive environments.
-
Platform dependency: Most VTubers rely heavily on platforms like YouTube, Twitch or TikTok. Sudden algorithm changes, demonetization or account bans can drastically affect visibility and income.
-
Monetization challenges: Generating steady income as a VTuber isn’t guaranteed. Success depends on audience growth, sponsorships and fan support — all of which can take years to build.
-
High upfront costs: Creating a professional-grade 2D or 3D avatar, along with streaming equipment and software, often requires significant financial investment before any returns are made.
-
Intense market competition: As the VTuber space grows globally, it becomes harder for new creators to stand out without a unique niche, strong branding or technical polish.
-
AI impersonation and deepfakes: In 2025, advanced AI tools make it easier for bad actors to clone VTuber voices or designs, increasing the risk of content theft, brand damage or viewer confusion.
So, becoming a VTuber in 2025 offers creative freedom, global reach and new career paths — but it’s not without challenges. From financial risks to mental strain and evolving tech threats, success requires more than just a good avatar. Do your research, protect your privacy, and approach the journey with both passion and preparedness.
-

Market maker deals are quietly killing crypto projects
The right market maker can be a launchpad for a cryptocurrency project, opening the door to major exchanges and providing valuable liquidity to ensure a token is tradeable — but when the wrong incentives are baked into the deal, that market maker can become a wrecking ball.
One of the most popular and misunderstood offerings in the market-making world is the “loan option model.” This is when a project lends tokens to a market maker, who then uses them to create liquidity, improve price stability, and help secure listings at a cryptocurrency exchange. In reality, it has been a death sentence for many young projects.
But behind the scenes, a number of market makers is using the controversial token loan structure to enrich themselves at the expense of the very projects they’re meant to support. These deals, often framed as low-risk and high-reward, can crater token prices and leave fledgling crypto teams scrambling to recover.
“How it works is that market makers essentially loan tokens from a project at a certain price. In exchange for those tokens, they essentially promise to get them on big exchanges,” Ariel Givner, founder of Givner Law, told Cointelegraph. “If they don’t, then within a year, they repay them back at a higher price.”
What often happens is that market makers dump the loaned tokens. The initial sell-off tanks the price. Once the price has cratered, they buy the tokens back at a discount while keeping the profit.
Source: Ariel Givner
“I haven’t seen any token really benefit from these market makers,” Givner said. “I’m sure there are ethical ones, but the bigger ones I’ve seen just destroy charts.”
The market maker playbook
Firms like DWF Labs and Wintermute are some of the best-known market makers in the industry. Past governance proposals and contracts reviewed by Cointelegraph suggest that both firms proposed loan option models as part of their services — though Wintermute’s proposals call them “liquidity provision” services.
DWF Labs told Cointelegraph that it doesn’t rely on selling loaned assets to fund positions, as its balance sheet sufficiently supports its operations across exchanges without relying on liquidation risk.
“Selling loaned tokens upfront can damage a project’s liquidity — especially for small- to mid-cap tokens — and we’re not in the business of weakening ecosystems we invest in,” Andrei Grachev, managing partner of DWF Labs, said in a written response to Cointelegraph’s inquiry.
Related: Who’s really getting rich from the crypto bull run?
While DWF Labs emphasizes its commitment to ecosystem growth, some onchain analysts and industry observers have raised concerns about its trading practices.
Wintermute did not respond to Cointelegraph’s request for comment. But in a February X post, Wintermute CEO Evgeny Gaevoy published a series of posts to share some of the company’s operations with the community. He bluntly stated that Wintermute is not a charity but in the “business of making money by trading.”
Source: Evgeny Gaevoy
What happens after the market maker gets the tokens?
Jelle Buth, co-founder of market maker Enflux, told Cointelegraph that the loan option model is not unique to the well-known market makers like DWF and Wintermute and that there are other parties offering such “predatory deals.”
“I call it information arbitrage, where the market maker very clearly understands the pros and cons of the deals but is able to put it such that it’s a benefit. What they say is, ‘It’s a free market maker; you don’t have to put up the capital as a project; we provide the capital; we provide the market-making services,’” Buth said.
On the other end, many projects don’t fully understand the downsides of loan option deals and often learn the hard way that they weren’t built in their favor. Buth advises projects to measure whether loaning out their tokens would result in quality liquidity, which is measured by orders on the book and clearly outlined in the key performance indicators (KPIs) before committing to such deals. In many loan option deals, KPIs are often missing or vague when mentioned.
Cointelegraph reviewed the token performance of several projects that signed loan option deals with market makers, including some that worked with multiple firms at once. The outcome was the same in those examples: The projects were left worse off than when they started.
Six projects that worked with market makers under the loan option agreement tanked in price. Source: CoinGecko
“We’ve worked with projects that were screwed over after the loan model,” Kristiyan Slavev, co-founder of Web3 accelerator Delta3, told Cointelegraph.
“It’s exactly the same pattern. They give tokens, then they’re dumped. That’s pretty much what happens,” he said.
Not all market-maker deals end in disaster
The loan option model isn’t inherently harmful and can even benefit larger projects, but poor structuring can quickly turn it predatory, according to Buth.
A listings adviser who spoke to Cointelegraph on the condition of anonymity echoed the point, emphasizing that outcomes depend on how well a project manages its liquidity relationships. “I’ve seen a project with up to 11 market makers — about half using the loan model and the rest smaller firms,” they said. “The token didn’t dump because the team knew how to manage price and balance the risk across multiple partners.”
The adviser compared the model to borrowing from a bank: “Different banks offer different rates. No one runs a money-losing business unless they expect a return,” they said, adding that in crypto, the balance of power often favors those with more information. “It’s survival of the fittest.”
But some say the problem runs deeper. In a recent X post, Arthur Cheong, founder of DeFiance Capital, accused centralized exchanges of feigning ignorance of artificial pricing fueled by token projects and market makers working in lockstep. “Confidence in the altcoin market is eroding,” he wrote. “Absolutely bizarre that CEXs are turning an absolute blind eye to this.”
Still, the listings adviser maintained that not all exchanges are complicit: “The different tier exchanges are also taking really extreme actions against any predatory market makers, as well as projects that might look like they rugged. What exchanges do is they actually immediately lock up that account while they do their own investigation.”
“While there is a close working relationship, there is no influence between the market maker and the exchange of what gets listed. Every exchange would have their own due diligence processes. And to be frank, depending on the tier of the exchange, there is no way that there would be such an arrangement.”
Related: Crypto’s debanking problem persists despite new regulations
Rethinking market maker incentives
Some argue for a shift toward the “retainer model,” where a project pays a flat monthly fee to a market maker in exchange for clearly defined services rather than giving away tokens upfront. It’s less risky, though more expensive in the short term.
“The retainer model is much better because that way, market makers have incentives to work with the projects long term. In a loan model, you get, like, a one-year contract; they give you the tokens, you dump the tokens, and then one year after that, you return the tokens. Completely worthless,” Slavev said.
While the loan option model appears “predatory,” as Buth put it, Givner pointed out that in all these agreements, both parties involved agree to a secure contract.
“I don’t see a way that, at this current time, this is illegal,” Givner said. “If somebody wanted to look at manipulation, that’s one thing, but we’re not dealing with securities. So, that gray area is still there in crypto — [to] some extent the Wild West.”
The industry is becoming more aware of the risks tied to loan option models, especially as sudden token crashes increasingly raise red flags. In a now-deleted X post, onchain account Onchain Bureau claimed that a recent 90% drop in Mantra’s OM token was due to an expiring loan option deal with FalconX. Mantra denied the claim, clarifying that FalconX is a trading partner, not its market maker.
Edited LinkedIn copy of Onchain Bureau’s LinkedIn post. Source: Nahuel Angelone
But the episode highlights a growing trend: The loan option model has become a convenient scapegoat for token collapses — often with good reason. In a space where deal terms are hidden behind NDAs and roles like “market maker” or “trading partner” are fluid at best, it’s no surprise the public assumes the worst.
“We’re speaking up because we make money off the retainer model, but also, this [loan option model] is just killing projects too much,” Buth said.
Until transparency and accountability improve, the loan option model will remain one of crypto’s most misunderstood and abused deals.
Magazine: What do crypto market makers actually do? Liquidity or manipulation